Piping fittings in the process industry include elbows, tees, reducers, and flanges, each serving a specific connection function. Material compatibility (stainless steel, PVC, brass) must be considered based on media characteristics and operating conditions. Selecting fittings that match the pipe diameter, pressure rating, and thread standard ensures system integrity. Temperature, pressure, and chemical factors significantly influence fitting selection. Compliance with ISO, ASME, and FDA standards ensures safety and compliance during installation.
Key points
- Common pipe fittings include elbows, tees, reducers, and flanges, each with specific functions in redirecting and connecting fluids.
- Material selection requires evaluation of compatibility, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific chemicals and operating environments.
- Dimensional accuracy and correct sizing ensure system integrity, with fittings that meet nominal pipe diameters and pressure requirements.
- Operating conditions such as temperature, pressure and fluid composition have a direct impact on fitting material selection and performance requirements.
- Regulatory compliance with standards such as ASME, ISO and industry-specific certifications ensures the safety and reliability of piping systems.
Understand the main types of pipe fittings in the process industry
Piping fittings are the backbone of all process engineering systems—critical components ensuring fluid integrity in complex piping networks.
You’ll encounter several important types of fittings, each playing a specific role in your system.
Bends change fluid flow direction at precise angles (typically 45° or 90°), minimizing pressure loss and turbulence. Bends are crucial when space constraints need to be overcome without compromising flow efficiency.
Various tees enable tee connections. Standard tees have identical openings, while reducing tees accommodate different pipe sizes.
For diameter transitions, reducers (concentric and eccentric reducers) ensure smooth connections between pipe sizes, preventing efficiency losses and cavitation.
Flanges enable bolted connections between pipes, valves, and equipment components and allow for disassembly during maintenance—essential for system lifespan and maintainability. Choosing the right hydraulic fittings can significantly improve piping system performance.
2. Material considerations for industrial pipe connections
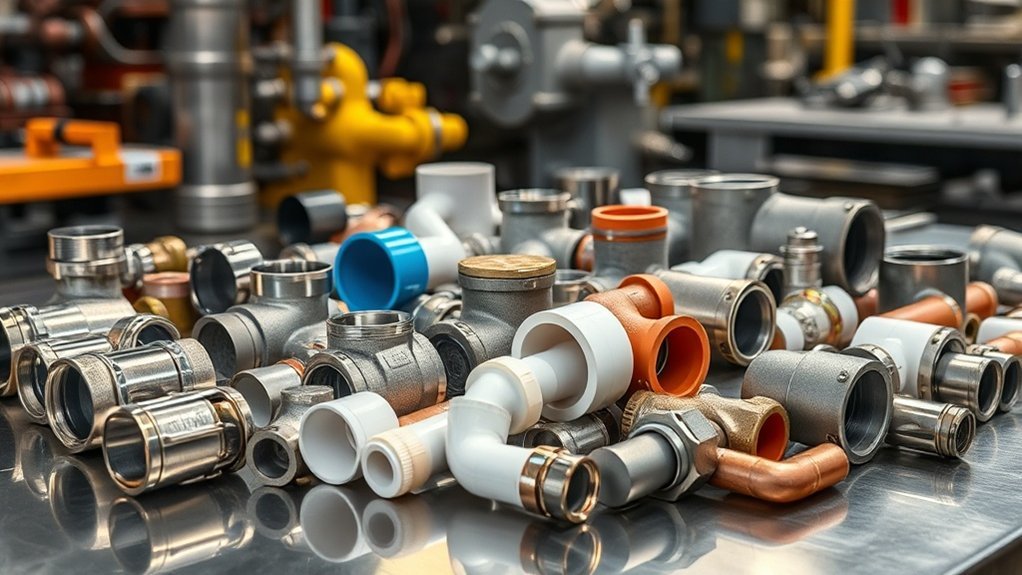

The selection of materials represents the foundation of a piping system design efficient, with a direct impact on performance, longevity and safety in industrial applications.
When evaluating connection options, you will need to prioritize material compatibility to prevent galvanic corrosion, especially evident when joining dissimilar metals such as copper tubing, where the brass fittings offer optimal protection.
316 stainless steel provides corrosion resistance superior in aggressive environments and resists high temperatures, while PVC guarantees excellent performance chemical resistance for wastewater applications, although requires adhesive fixing.
Brass fittings excel at joining different materials in various fluid conveying scenarios.
For extreme conditions, temperature considerations may be necessary special alloys such as Inconel 625, which provides greater protection against corrosive chemicals.
Also, respect for materials and standards it is essential to ensure the reliability and efficiency of the piping system.
Your material selection must balance operational requirements, environmental factors and long-term reliability to ensure thesystem integrity.
3. Size and dimensional requirements for optimal performance
When choosing pipe fittings, dimensional accuracy becomes the foundation of the system’s integrity, directly influencing flow characteristics, pressure resistance capacity and long-term reliability.
You must ensure that the fittings exactly match the nominal diameter of the pipe to maintain flow efficiency in the system. Connection points should slightly exceed the pipe diameter, allowing for thermal dynamics while facilitating simple installation.
Remember this compatibility of fittings goes beyond size: pressure ratings must be in line with system requirements, typically up to 300 PSI at 150°C for Class 150 malleable iron fittings. Standards and solutions for efficient industrial plumbing systems are essential to ensure optimal performance.
Thread standards should not be overlooked; Incompatibilities between NPT and BSP can lead to critical failures. Furthermore, you will get optimal adaptation performance while maintaining recommended flow speeds (2-3 m/s for water), thus avoiding turbulence which accelerates wear and reduces system efficiency.
4. Operating conditions and their impact on the choice of fittings
Why system integrity depends directly on environmental factors, operating conditions serve as primary determinants in selecting appropriate pipe fittings.
You will have to take this into account the effects of temperature in material selection: Stainless steel performs exceptionally well in high-temperature environments due to its strength and corrosion-resistant properties.
The pressure classes should correspond to the system requirements; 150 rated malleable iron fittings can withstand up to 300 PSI at 150°C.
THE chemical composition of the fluids transported dictates the material compatibility : PVC works well for wastewater, while brass is suitable for lubricants and water systems.
For harsh chemical environments, 316 stainless steel provides optimal protection, while nylon fittings are preferred for flammable fluids.
Regular evaluation of these operating parameters is essential, as it often leads to poor material selection system failures and costly losses.
5. Installation standards, certifications and good practices
Since regulatory compliance compliance with standards is essential for the safety and reliability of systems industrial standards and certifications remain non-negotiable during the selection and installation of pipe fittings.
It is necessary to verify that the connections comply with the ISO standardsASME e FDAparticularly for food processing and pharmaceutical applications. The main certification processes include CE marking for European markets and ANSI/NSF for drinking water systems, confirming material compatibility and performance indicators.
During the installation of the fittings it is necessary to follow the instructions scrupulously installation guidelines by the manufacturer. This includes using specific tools, ensuring proper alignment and meeting torque specifications.
Regular inspection protocols should be implemented to identify potential wear, corrosion or leaks. By using certified components and following established installation protocols, you will minimize operational interruptions while maximizing system efficiency and regulatory compliance.
latest posts published

Citroën ë-Jumpy won the prestigious Millésime Trophy

The purpose and function of the stabilizer

Maintenance of vehicles (transporting dangerous goods)

The Lithuanian jubilee elections for “Car of the Year” have begun

Volkswagen presented the updated T-Roc

An intelligent wildlife warning system for motorists

Features of electric car charging with a simple click

Four ways to identify a sunken car

In the new city – 2 kilometers of new cycle paths, pedestrian paths are being renovated